The world of Bitcoin is filled with technical terms that can seem complex at first glance. One of these terms is the Bitcoin “mempool.“
But what exactly is it, and why is it so important in the context of Bitcoin transactions?
When you send Bitcoin to someone, the transaction isn’t processed immediately. Instead, it’s broadcast to the network and waits its turn to be included in a block on the blockchain. Once miners add your transaction to a block, it’s considered confirmed.
But where exactly does your transaction wait before reaching this stage? That’s where the Mempool comes in!
Mempool: the waiting room for Bitcoin transactions
“Mempool” is a combination of “memory” and “pool.” Essentially, it represents the “waiting room” for Bitcoin transactions. All unconfirmed transactions remain in the mempool until they are selected by miners to be included in a block.
Here are some key points to help you better understand this pool of unconfirmed transactions:
- Pending Transactions: When you send Bitcoin, your transaction is first sent to the mempool, where it waits to be picked up by a miner.
- Transaction Fees: You can opt to pay a higher fee to have your transaction processed faster. Transactions with higher fees are generally more attractive to miners because they receive these fees as rewards. So, if the transaction pool is crowded, those with higher fees are more likely to be processed first.
- Mempool Size: The size of the mempool fluctuates. If many people are transacting at the same time, it can become congested, causing delays unless you pay a higher fee to move ahead in the queue.
How did the Mempool come about?
The Mempool is part of BIP 35, a Bitcoin Improvement Proposal introduced in 2012. This proposal was designed to allow external nodes to access the Mempool of other nodes, which is useful in several situations:
- For SPV clients (Simplified Payment Verification), also known as lightweight wallets, that want to view transactions before they are officially confirmed and added to a block.
- For miners looking to assess the most profitable fees or access the current list of pending transactions to begin confirming them.
- For remote network diagnostics.
The mempool plays a crucial role in the Bitcoin ecosystem. By monitoring it, we can estimate how long it will take for a transaction to be confirmed based on the fees paid and the number of pending transactions.
How many transactions fit in the Mempool?
The capacity of the Mempool, in terms of the number of transactions, isn’t fixed and isn’t determined by the Bitcoin protocol. Instead, the mempool functions like a cache in individual nodes of the Bitcoin network, temporarily storing unconfirmed transactions as they wait to be included in a block.
The exact number of transactions it can hold depends on several factors, such as:
1. Node Configuration:
Each node operator can set the maximum mempool size based on available memory and performance preferences.
For example, a node operator might limit their mempool to 300 MB of transactions. When this limit is reached, the node may start dropping transactions with lower fees to make room for transactions with higher fees.
2. Transaction Size:
Bitcoin transactions vary in size. Some might be just 250 bytes, while others could be several kilobytes, depending on the complexity and number of inputs and outputs (UTXOs). As a result, the number of transactions that can fit in the mempool depends on the average size of the pending transactions.
3. Variation Among Nodes:
Keep in mind that each node on the Bitcoin network has its own mempool, and its contents can vary from one node to another. A transaction discarded by one node due to space limits may still be present in another node’s mempool.
Setting a mempool limit is mostly a practical decision. Running a full Bitcoin node requires resources, including RAM.
If the mempool were to grow indefinitely, it could consume all available memory, leading to performance issues or even crashes. By setting a limit, node operators can ensure their systems run smoothly and efficiently.
Additionally, a mempool limit can have an economic effect. By creating artificial scarcity of mempool space, users may be incentivized to pay higher fees to ensure their transactions are confirmed quickly, especially during times of high demand.
Because mempool settings are customizable, the content of each mempool can differ between nodes. While one node might drop transactions due to its limit, another node with a higher (or no) limit might still hold those transactions.
It’s important to note that transactions dropped by a node due to space limits in the mempool are not permanently rejected. If a transaction is important, it can be re-broadcast and may eventually reach a node with available mempool space, where it can then be included in a block.
Where to monitor Mempool activity?
If you’re interested in real-time mempool statistics, several blockchain explorers and dedicated websites offer detailed views, including the total number of transactions, updated fees, and total size in bytes.
Here are two well-known block explorers:
Blockstream.info
Blockstream.info is a block explorer for both the Bitcoin and Liquid Network blockchains. It was developed by Blockstream, the company behind the Jade wallet, which focuses on developing Bitcoin technologies and solutions.
Mempool.space
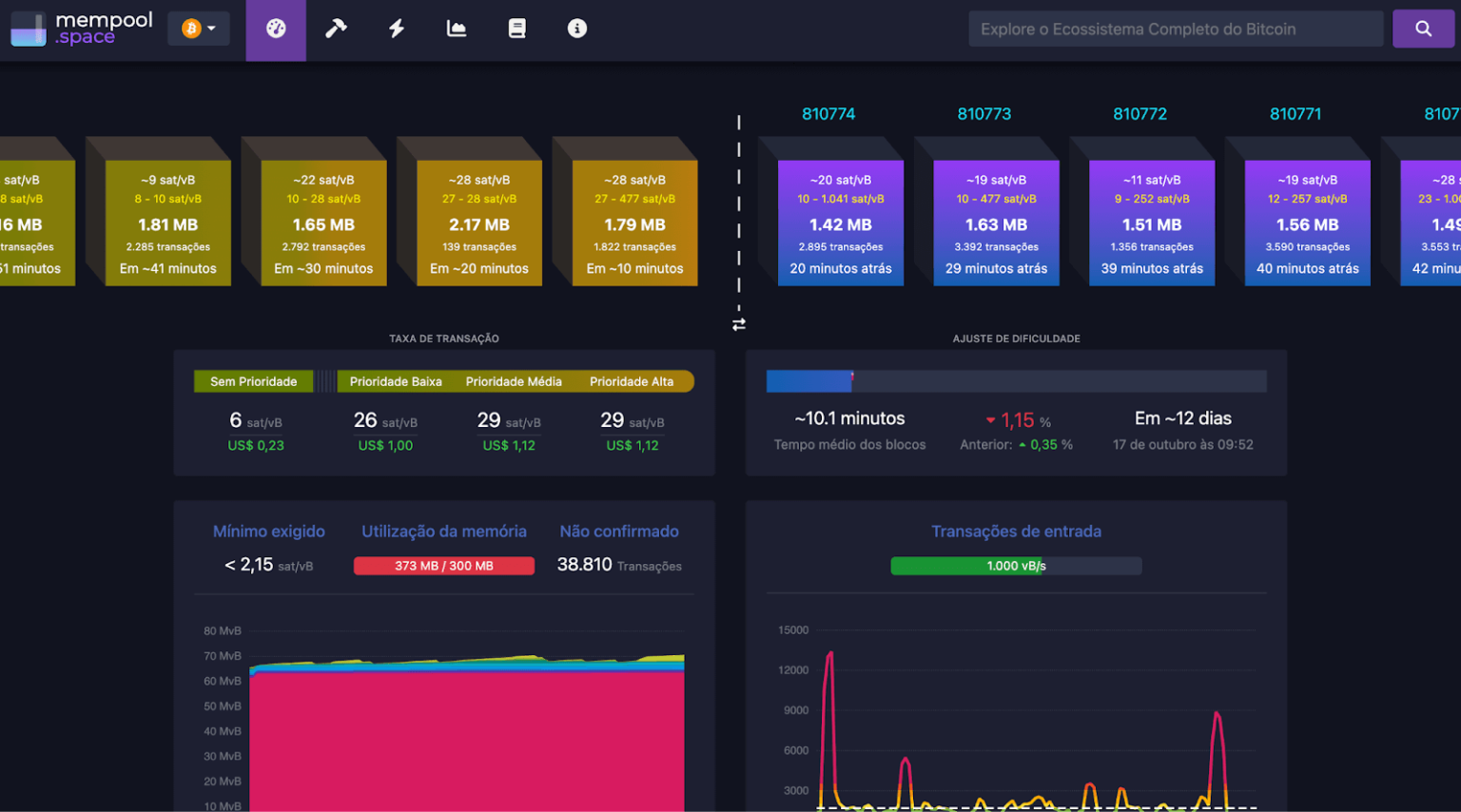
Mempool.space is another popular Bitcoin blockchain explorer and mempool viewer.
Its interface is impressive, and unlike other block explorers that mainly focus on past blocks and confirmed transactions, mempool.space offers a detailed view of the current state of the mempool. This is especially useful for those who want to understand real-time transaction fees, estimate confirmation times, and assess the overall health of the network.
When choosing a tool to monitor the mempool, it’s helpful to check if it provides the specific details you need.
Keep in mind that the mempool situation can change quickly depending on the volume of transactions and other network conditions.
For those with technical expertise or who want more privacy or specific information, it’s also possible to run your own Bitcoin node and access the mempool directly through commands or interfaces connected to your node.
Mempool congestion
On average, the Bitcoin network adds a new block of transactions every 10 minutes. However, this is just an average, and in practice, if the mempool is congested, it can take hours for your transaction to be processed.
The time it takes for your transaction to be confirmed largely depends on the fee associated with it.
Mempool congestion occurs when there’s a significant increase in the number of transactions being submitted to the Bitcoin network, but miners cannot process them quickly enough to include them in new blocks.
This congestion can be caused by several factors, such as:
Sudden Increase in Transactions
A sudden surge in demand for Bitcoin transactions, whether due to rapid price changes or large fund movements, can result in a high volume of transactions within a short period.
Block Size Limitation
Bitcoin blocks are limited in size.
Originally, the limit was 1 MB, but with the implementation of SegWit, the effective capacity increased to 4 MB. This means only a certain number of transactions can be included in each block. So, if there are more transactions than available space, some will have to wait.
Fee Strategy
During periods of congestion, many users may choose to increase their fees to ensure faster confirmation. This can result in an overall increase in fees, causing lower-fee transactions to wait longer for processing.
Spam Attacks
At times, malicious actors have flooded the network with a large number of low-value transactions (often with very low fees) to intentionally clog the network. These are known as spam attacks and can cause temporary congestion.
Fortunately, the Bitcoin network’s proof-of-work consensus mechanism progressively makes spam attacks more costly, discouraging such actions on the network.
Adoption of New Technologies
The launch or widespread adoption of new technologies or applications using the Bitcoin blockchain can lead to transaction spikes, causing mempool congestion.
For example, in May 2023, the Bitcoin network reached significant milestones: the mempool peaked with 400,000 pending transactions, and transaction fees surged by 60% in less than a week, from $4.40 to $6.90.
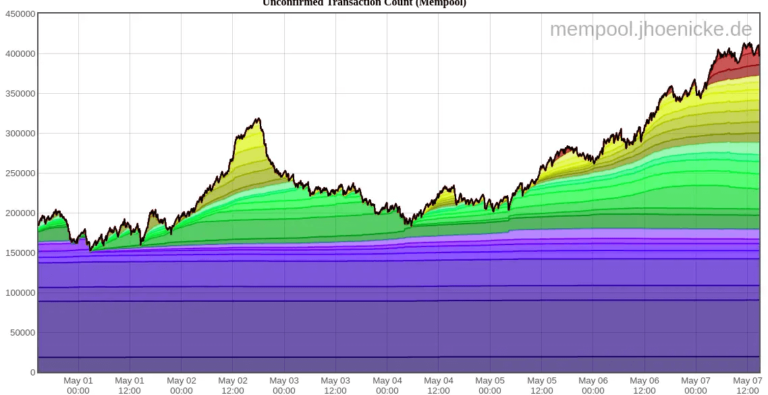
Previously, the record for unconfirmed transactions was set in January 2018, when it exceeded 250,000.
The spike in Bitcoin transactions was driven by the Ordinals project, a controversial initiative that allows NFT-like media to be inscribed on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Mempool congestion is usually temporary. As blocks are mined and transactions are confirmed, space is freed up. However, during periods of high demand, congestion can last longer.
What to do if your transaction gets stuck in the Mempool?
If your transaction gets stuck in the mempool due to a very low fee, it may not be picked up by miners. To resolve this, you can replace the previous fee with a higher one, speeding up your transaction’s confirmation.
Here are some ways to do this:
- Use the Replace-by-Fee (RBF) Function: Some wallets, like Electrum and Blue Wallet, offer the option to replace a pending transaction with a new one by paying a higher fee.
- Use Transaction Accelerators: Some mining pools provide services to accelerate specific transactions, either for a fee or on a first-come, first-served basis.
Does the Mempool track transactions on the Lightning Network?
No, the mempool does not track transactions on the Lightning Network. It is associated with the Bitcoin blockchain and refers to the set of unconfirmed transactions waiting to be included in a block. Therefore, it specifically tracks transactions that occur on Bitcoin’s base layer.
The Lightning Network, however, is a second-layer solution built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain to enable faster and cheaper transactions. Transactions on the Lightning Network do not appear directly in the Bitcoin mempool, as they are not immediately recorded on the main blockchain. Only when Lightning channels are opened, closed, or updated are these transactions recorded and confirmed on the blockchain, passing through the mempool in this process.
Thus, while the mempool is used to monitor and prioritize unconfirmed transactions on Bitcoin, it does not provide visibility or tracking for individual transactions within the Lightning Network.
Conclusion
The mempool is an essential component of the Bitcoin network, ensuring that all transactions are processed in order and allowing users to monitor network activity in real time.
Additionally, understanding how it works can help you make more informed decisions about when and how to send Bitcoin, potentially saving on fees.
We hope this article helped you understand the mempool and its importance. If you want to dive deeper into Bitcoin, its functionality, and fundamentals, the best way is through Bitcoin Starter, the most comprehensive and highly rated Bitcoin course in the world.
Don’t forget to share this post with friends. Until next time, and opt out!
Share on your social networks:

Founder of Area Bitcoin, one of the largest Bitcoin education projects in the world, she is a marketer, passionate about technology, and a full-time hands-on professional. She has participated in major Bitcoin conferences such as Adopting Bitcoin, Satsconf, Surfin Bitcoin, and Bitcoin Conference.
Did you like this article? Consider buying us a cup of coffee so that we can keep writing new content! ☕







