Most people know about Bitcoin, but they might not realize that there are several ways to transact, send, and receive money using the Bitcoin network.
In this article, we’ll help you understand the differences between on-chain Bitcoin transactions and transactions on the Lightning Network, which is the fastest and cheapest way to send Bitcoin.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Understanding Bitcoin On-Chain
Bitcoin works in layers, and to make it easier, you can think of Bitcoin as a building. Layer one is the blockchain layer, the foundation of the building. It is the network that supports all the security and decentralization of the protocol.
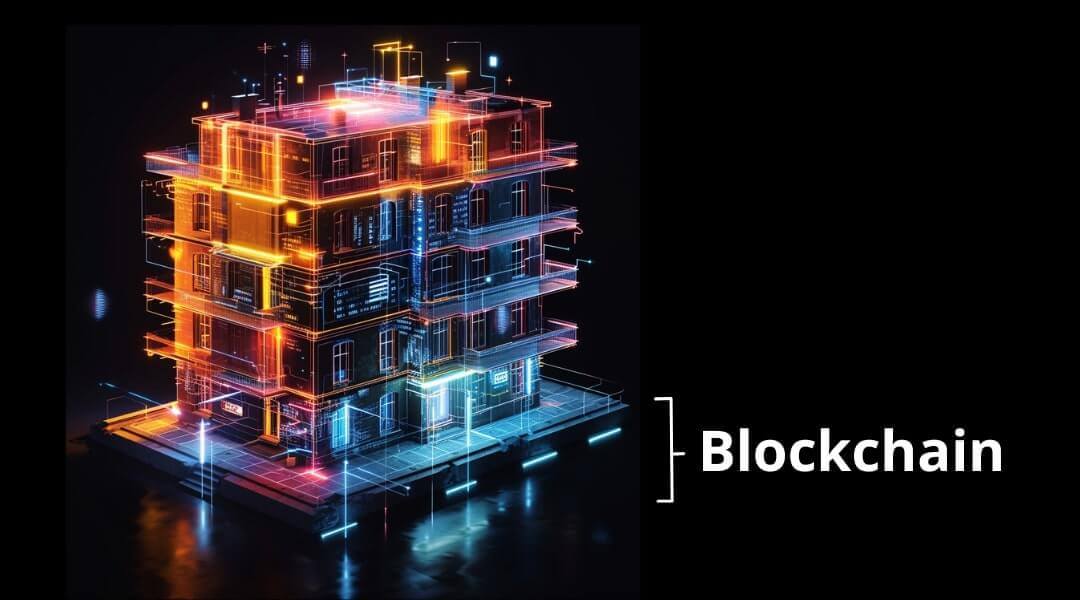
Bitcoin is revolutionary because, for the first time, a computer network is able to create digital money independent of banks and governments. To achieve this, the Bitcoin protocol uses several mechanisms such as proof of work (mining), difficulty adjustment, cryptography, digital signatures, and nodes that connect the network, verify records, and store copies of the blockchain across the world.
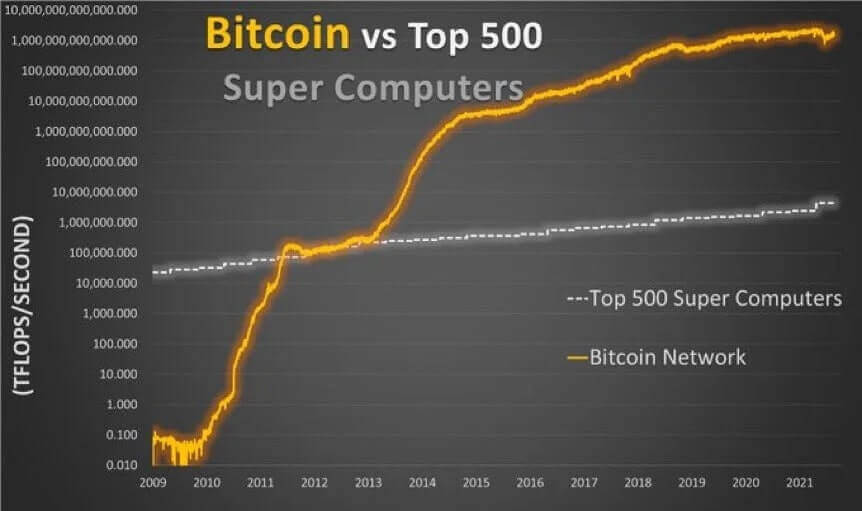
This layer is completely dedicated to preserving the fundamentals of Bitcoin as a network that cannot be hacked, invaded, or modified by anyone, as it has more computing power than the 500 most powerful computers in the world combined!
Furthermore, this layer maintains the principles of Bitcoin as a solid currency, with a limit of 21 million units that can be created. That’s why Bitcoin is a predictable currency that does not suffer from infinite inflation like fiat money.
However, such a secure and decentralized blockchain cannot be fast and cheap all the time. Each block that processes transactions sent by users can take 5, 10 minutes, or even hours to mine. This variation in time depends on the number of transactions waiting to be included in the block by a miner and the difficulty of mining each block at that time.
Difficulty adjustment is a mechanism in the Bitcoin network that maintains predictability in the issuance of new bitcoins, ensuring that even if many miners connect to the network or if a miner with a very powerful machine participates, they will not be able to mine all the bitcoins at once.
The Bitcoin network has reached records in computational power, which increases the difficulty of mining each block to keep Bitcoin’s properties immutable.
One way the network selects which transactions will have priority when demand is very high is by charging a higher processing fee for those with more urgency. As the network does not intend to change its fundamentals and, over time, the demand for transactions tends to increase, Bitcoin network fees at the on-chain layer are expected to become more expensive in the future. This will help maintain miners’ revenue as halvings reduce the block reward.
In this sense, layer one will become a final settlement layer, where the highest volume transactions occur, while smaller payments will be made in adjacent layers focused on scalability, such as the Lightning Network.
Now that we’ve talked about layer one, the Bitcoin blockchain, which is the foundation of the building, let’s understand the Lightning Network.
What is Bitcoin’s Lightning Network
The lightning network is a layer two of Bitcoin. This network is based on layer one and allows you to make instant payments almost for free. It’s like the first and second floors of the Bitcoin building.
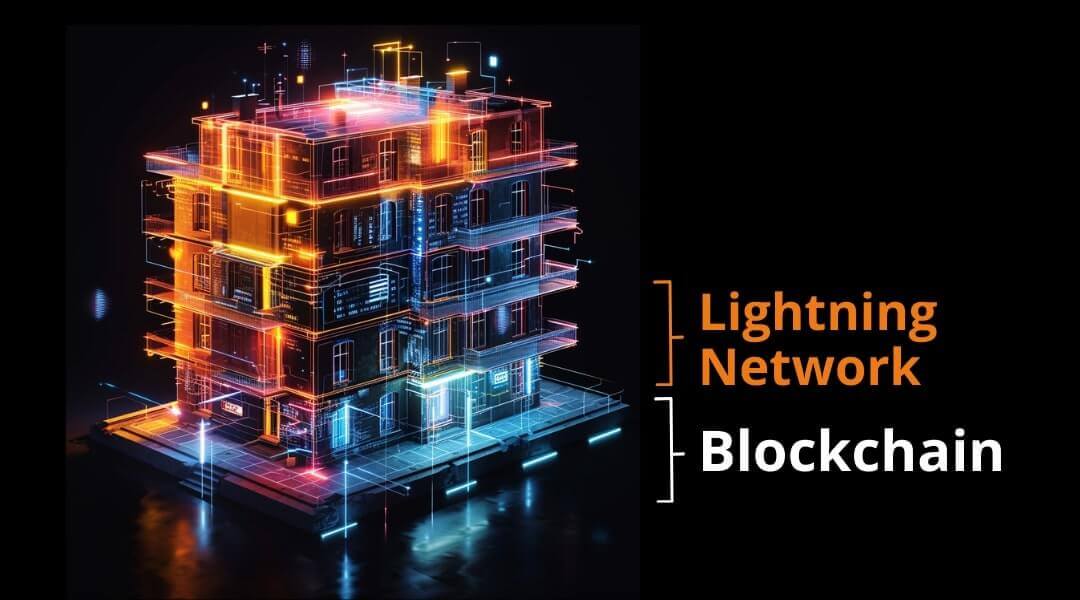
At this point, most users will access the “building” and head to their desired floor.
You can go to the third floor, where more complex contracts take place, or to the fifth floor, where in the future, it will be possible to carry out Bitcoin collateralization contracts on the Lightning Network without intermediaries.
The Lightning Network aims to enhance the characteristics of Bitcoin through a network of P2P payment channels, without requiring all payments to be recorded on the blockchain.
These channels make Lightning payments as fast as lightning and interconnect, making Bitcoin the most efficient global financial network in existence. It gives power back to the people, allowing them to use their money however they want, without depending on banks or governments.
That’s the theory, but how does it work in practice? The time has come to show you!
We will demonstrate two types of Bitcoin transactions: one on-chain and one on the Lightning Network, so you can understand the differences. To do this, we will use vouchers from Azteco, purchased on the azte.co website, and I will redeem them in my own Bitcoin on-chain and Lightning wallets.
Don’t know Azteco? Then, check out our article: Is it worth buying Bitcoin through Azteco?
This way, you will be able to understand the processing times and different methods when purchasing Bitcoin on-chain or on the Lightning Network and sending it to your wallet using different types of networks.
This will also help you understand how it works when receiving a payment from someone, giving you a sense of how long the network takes to process and how to verify transactions.
Using Bitcoin On-Chain in practice
First, let’s send Bitcoin on-chain, which is layer one of Bitcoin, and understand the times and fees associated with this network. To carry out the process, just follow the steps below:
- Go to azteco.co and click on ‘redeem’.

- Then, enter the on-chain voucher code that you have already purchased from Azteco.

- Now enter the on-chain address where Azteco should send the satoshis.
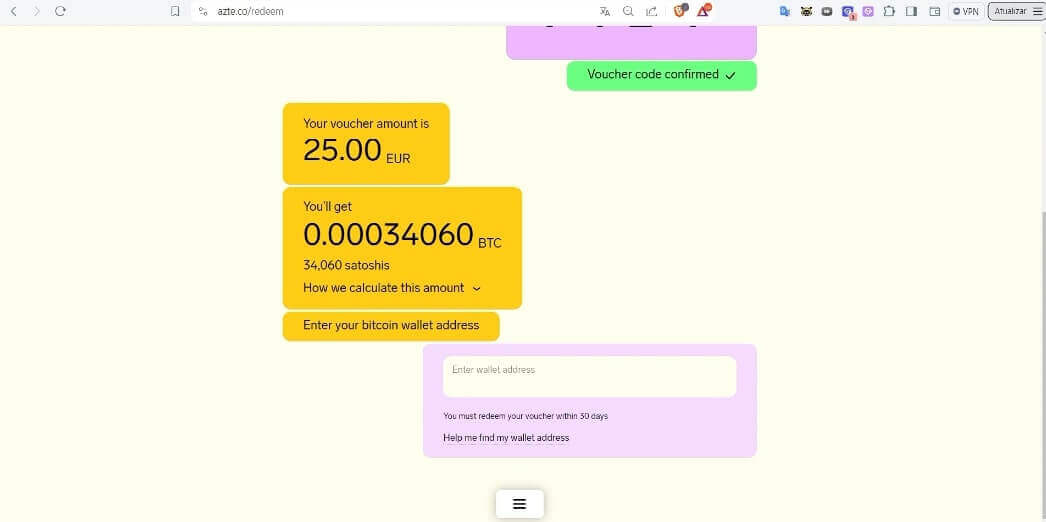
- After pasting the bitcoin on-chain address, the satoshis will automatically be sent to the specified wallet.

At the end, a screen will appear with a summary of the entire purchase, including the redeemed bitcoin balance, the Azteco commission, and the on-chain network fees, which was 97 euro cents.
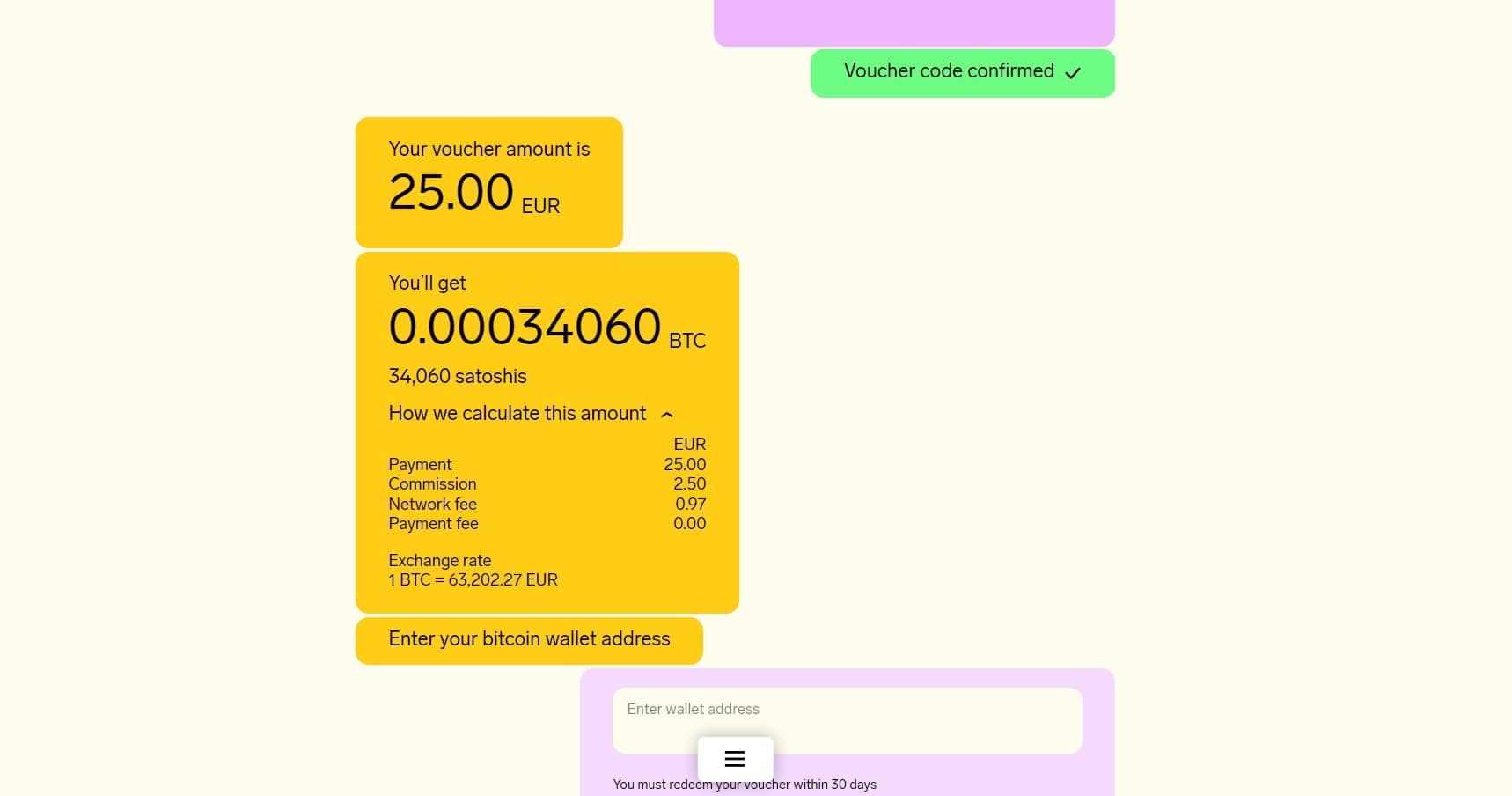
The last step is to paste the address where you want to receive the satoshis, wait for the transaction to be processed by the Bitcoin blockchain, and the balance to be confirmed at the specified wallet address.
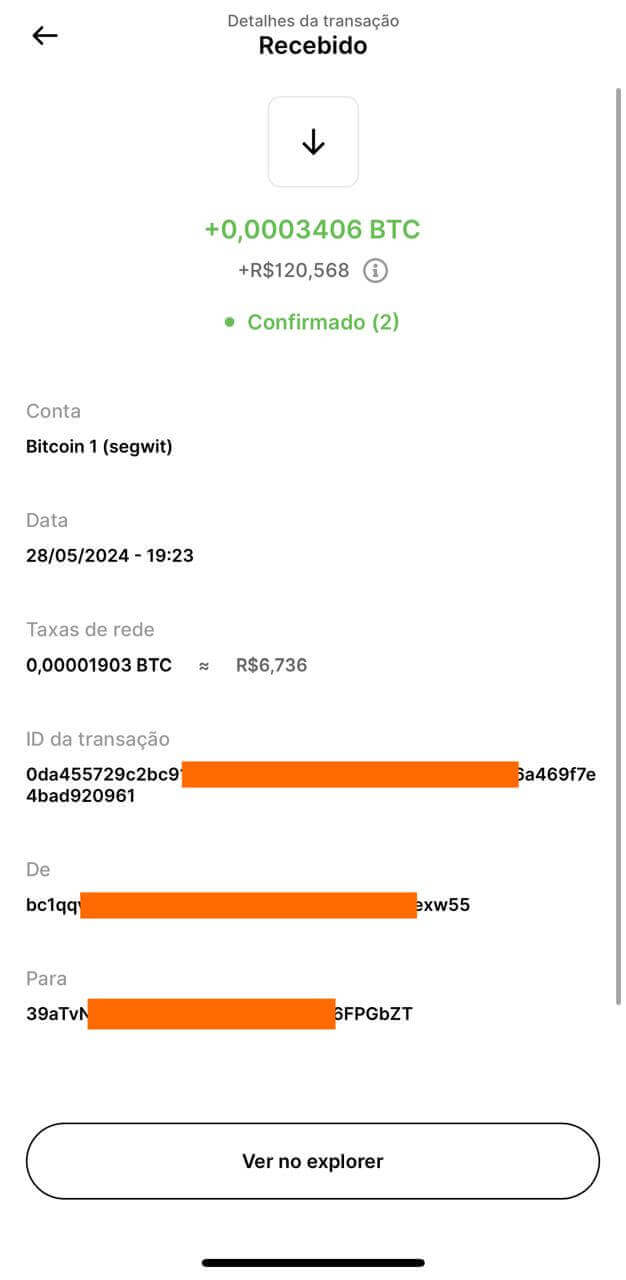
And the transaction was received! This Bitcoin on-chain transaction arrived very quickly, taking about 5 minutes. However, often, when there is a lot of demand for transactions on the network, it can take more than an hour for a transaction to be processed.
For example, on April 20th, when the fourth Bitcoin halving took place, transactions took hours and the fees were very expensive, more than $20 per transaction.
Note that in the Bitcoin on-chain network, the transaction is not immediate and may take a few minutes to complete.
Also, depending on the amount you want to send, the fee is often not worth it for smaller payments, such as a cup of coffee. A fee of $3 could be the price of the coffee itself! Therefore, the Lightning Network was created, allowing smaller payments, such as a coffee, without fees making the transaction unfeasible.
So now let’s see how sending via the Lightning Network works so you can see the difference in rates and speeds of each of these Bitcoin networks.
Using the Lightning Network in practice
Let’s go through the same process using Azteco.
- Go to azteco.co and click on “redeem“.

- Then, enter the Lighting voucher code that you have already purchased from Azteco.

The voucher is confirmed and the amount of 25 euros to be sent to my wallet is now available.

Notice how the “network fee” line is zero. This is because the Lightning network has virtually no fees, with only a few satoshis being worth less than a penny. Azteco does not even consider this value as relevant.
- Now let’s scan this QR Code with a lightning wallet. We’ll use the Blink wallet, which supports the Lightning network. Open the wallet and click “scan”. The camera will open, and you can scan the Lightning QR Code that appears on the computer screen.
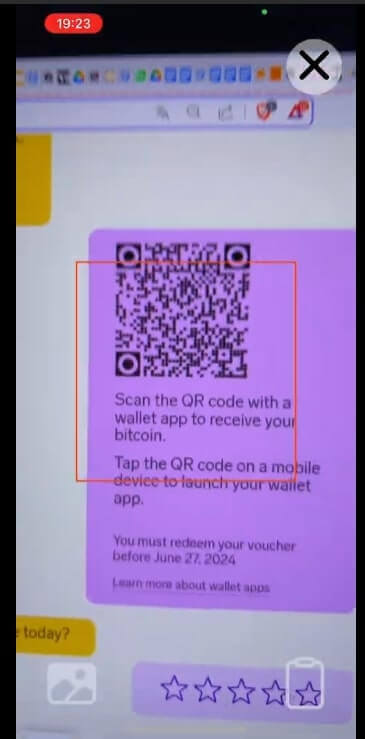
- A message appears in the Blink wallet confirming whether the balance is to be redeemed, showing that is an Azteco voucher worth 35,588 satoshis, exactly the balance of the lightning voucher purchased at Azteco. Now just click on “Redeem Bitcoin” for the amount to be received via Lightning in this wallet.

Once this is done, the transaction immediately appears in the wallet. In addition to being fast, it had a lower fee than the transaction made on-chain.

In the Blink wallet, you can see the details of this transaction, such as the time it took place (just 18 seconds ago), the fact that it was via Lightning, and other data such as pre-image, invoice, hash, and wallet identifier.
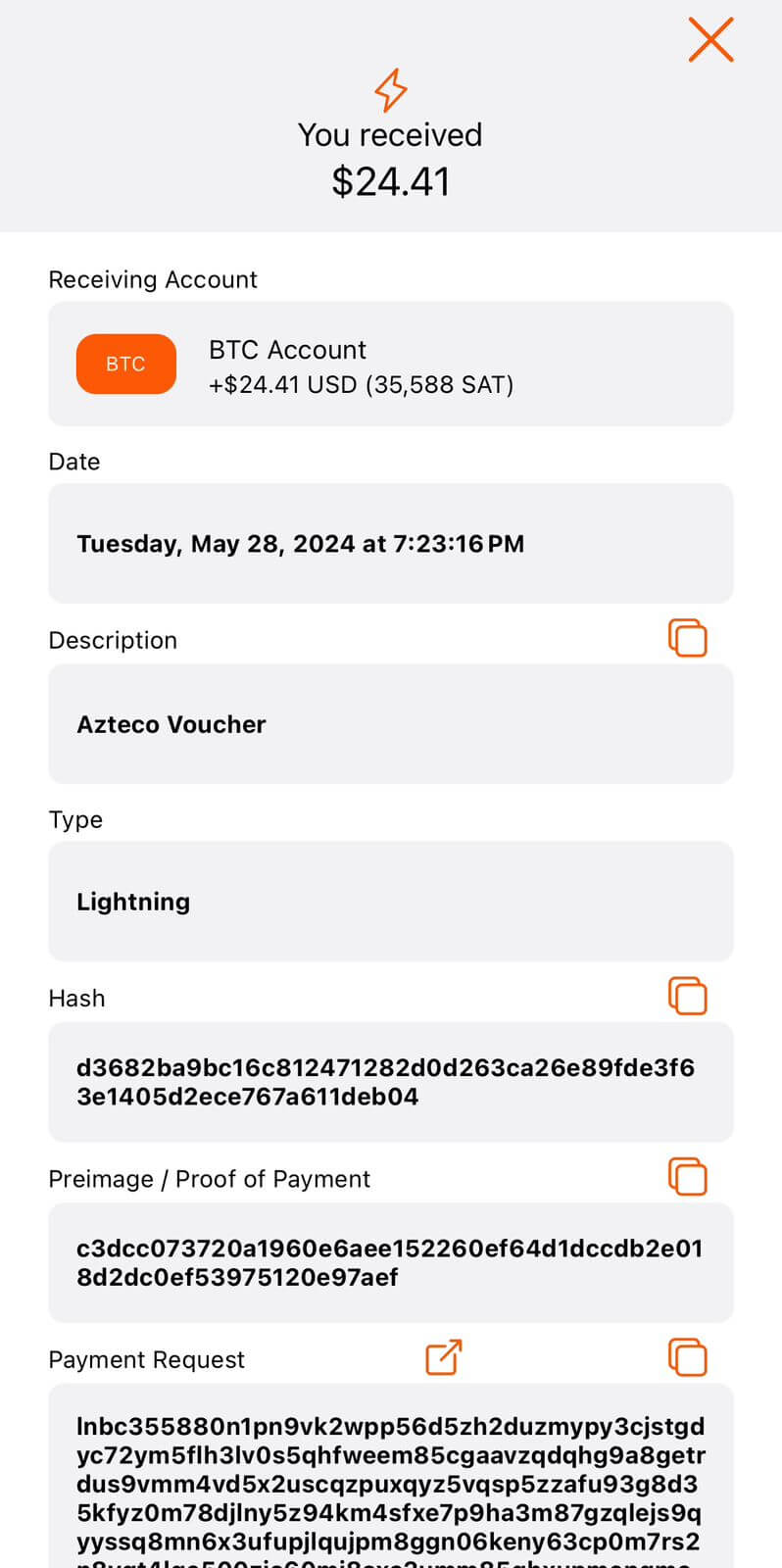
Notice how the transaction took just a few seconds, much faster than the bitcoin on-chain transaction, which took 5 minutes.
*There is a small variation in the amount of Bitcoin shown because my wallet is pricing Bitcoin in dollars instead of euros, showing $24.41.
Now that the balance has arrived, you can use your sats to make payments!
Conclusion
Do you notice the huge difference in processing time and fees between the layers of the Bitcoin network?
It’s important to highlight that each layer has a specific use. Layer one, the blockchain, is best suited for storing Bitcoin in the long term without relying on intermediaries. Layer two, the Lightning Network, is ideal for everyday payments and smaller amounts.
The Lightning Network is like the money you set aside for your daily or weekly needs, while the bitcoin on-chain layer is used to protect and store your Bitcoin, functioning as a digital vault.
When we think of gold, we imagine gold bars in a vault; at the bitcoin on-chain layer, this “gold” is digital, represented by Bitcoin. If you take good care of your keys, no one can steal it from you.
Each network has its own benefits and drawbacks, and choosing which one to use depends on your specific needs, such as security, convenience, cost, and transaction speed.
In summary:
- On-chain transactions take longer and have higher fees, but the network is safer for storing Bitcoin in the long term.
- Lightning transactions are instantaneous, with low, almost insignificant fees, making it ideal for everyday payments.
We hope this article has helped you understand the differences between bitcoin on-chain and Lightning. We suggest you try the same practice using Azteco vouchers to get the full experience of how Bitcoin networks work.
Until next time and opt out!
Share on your social networks:

Founder of Area Bitcoin, one of the largest Bitcoin education projects in the world, she is a marketer, passionate about technology, and a full-time hands-on professional. She has participated in major Bitcoin conferences such as Adopting Bitcoin, Satsconf, Surfin Bitcoin, and Bitcoin Conference.
Did you like this article? Consider buying us a cup of coffee so that we can keep writing new content! ☕