Keeping your satoshis secure is essential, and there are several wallets available, each serving different user needs. One of them is the Phoenix Wallet.
Phoenix is a non-custodial, mobile Lightning wallet offering tools for both beginners and advanced users. It’s also one of the most popular options for Lightning payments. While it recently withdrew from U.S. app stores, it continues to operate normally in Australia, the UK, and other countries.
In this article, we’ll explain how the Phoenix Wallet works and how to use it.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
The Lightning Network and Channel Management
Before diving into how the Phoenix Wallet works, it’s important to understand the basics of the Lightning Network and its channel management system.
The Lightning Network is a second-layer solution for Bitcoin, designed primarily for smaller, faster payments. When Lightning was launched in 2017, its usability was not well understood, but it has since seen significant improvements.
Lightning is an off-chain payment protocol, meaning it operates parallel to the Bitcoin blockchain using nodes and payment channels that connect users globally. Essentially, it’s a network linked to the blockchain, but not all transactions are recorded on the blockchain.
To illustrate, think of Bitcoin as a building where every floor is connected to the ground floor. Anyone entering or leaving must pass through the lobby and use the elevator to reach the desired floor. Similarly, higher layers like Lightning rely on the base layer for entry and exit points within the protocol.
How to open a Lightning channel
To open a Lightning channel, two parties need to lock funds (bitcoins) in a multisig address. This address requires multiple signatures to approve transactions, working like a joint Bitcoin account that prevents a single point of failure. This setup happens on layer 1, similar to passing through the building’s lobby.
The bitcoins locked on the blockchain represent the channel’s maximum capacity. For example, if you and I want to open a payment channel on the Lightning Network, we’ll need to deposit funds into a multisig address.
Within this channel, we can exchange value as long as it doesn’t exceed the total amount we locked.
It’s like having a prepaid tab at a bar—you can order anything as long as it’s within the prepaid limit.
When you want to close the tab and leave the bar (close the Lightning channel), you settle the bill at the cashier. Similarly, when a Lightning channel is closed, the final transaction is recorded on the blockchain, and the balance is settled.
In summary, the only transactions recorded on the blockchain are the opening and closing of the channel.
How does channel management work?
I can open a Lightning channel with you by depositing 2 bitcoins, and you do the same. This gives us a shared capacity of 4 bitcoins, allowing us to send satoshis instantly and at a very low cost, as long as we don’t exceed the total value.
Anyone can open a Lightning channel, as long as they understand the technical requirements, run a node, and lock bitcoins into the channel.
However, opening Lightning channels isn’t always cheap. Both parties need to contribute liquidity (capacity), meaning some funds get locked and can’t be spent outside the channel.
Additionally, these channels operate off the Bitcoin blockchain, enabling multiple transactions to occur within a single channel, which can later be settled as one transaction on the blockchain.
Closing channels can also be expensive, as Bitcoin network fees apply and vary depending on the time.
Channels have capacity limits, and if you reach the maximum, you’ll need to close the channel and open a new one. These processes can be complex for the average user, which is why Phoenix was designed to simplify channel management.
What company is behind the Phoenix Wallet?
The company behind the Phoenix Wallet is ACINQ, a French startup based in Paris focused on developing products and services for the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Since 2015, ACINQ has been contributing to the Lightning Network using its technology base called Eclair, a complete implementation of Lightning that allows users to run their own Lightning nodes.
ACINQ is known as a major liquidity provider and operator on the Lightning Network, running the largest node in the network. In 2017, they introduced Eclair Mobile, a Lightning-enabled wallet, though it had a more technical user interface.
To create a simpler experience, they redesigned it from the ground up and launched Phoenix—named after the mythical bird that rises from its ashes.
How did the Phoenix Wallet come about?
Phoenix Wallet was launched on December 12, 2019, to address the need for a more user-friendly experience on the Lightning Network. It was designed to provide users with a simple and accessible interface, making it easier to interact with Lightning payments.

Features of the Phoenix Wallet
When Phoenix launched with version 1.0, it was considered a second-generation wallet, offering a significantly better user experience compared to ACINQ’s earlier Eclair Mobile wallet.
Some of its initial features included:
- Automatic Channel Opening: Phoenix automatically opens a new channel if there’s not enough inbound liquidity to receive a payment.
- Turbo Channels: It allows you to use a Lightning channel as soon as it’s created, without waiting for confirmation of the channel’s opening.
- Backup of Peers: Previously, to back up a Lightning wallet, you needed to back up all channels; with Phoenix, just back up the wallet’s 12 words, and your money will be there.
- Zero Reserve + AMP: It allows you to spend your money as a single balance, even if it’s internally distributed across multiple Lightning channels.
- Cross-Network Swaps: Send and receive on-chain transactions seamlessly, even if you’re using the Lightning network.
- “Trampoline” Payments: Phoenix finds the closest payment route to connect with another wallet’s node to make a payment, without needing a direct node between sender and receiver.
Additionally, Phoenix is a self-custody wallet, meaning you control your private keys and are responsible for securing them.
While these features provide a more user-friendly experience, they also come with certain trade-offs.
What are the Trade-offs?
First of all, Trade-offs are compromises made to prioritize certain features or choices, often at the expense of others.
In the case of Phoenix, one trade-off is that it only connects to ACINQ’s nodes, meaning that payment data (such as value and destination) is shared within ACINQ’s network. While this setup improves reliability and simplifies channel management, it comes at the cost of reduced privacy and network independence.
How is backup handled in Phoenix?
Backing up a traditional Bitcoin wallet is straightforward since you only need to secure the private key. However, with Lightning wallets, backups were more complex as they needed to be updated with each transaction.
From a Lightning protocol perspective, restoring an outdated backup is seen as cheating, allowing the counterparty to potentially seize all funds in the channel.
There are static backups, but they have two problems:
- you need to make a backup every time you open a channel.
- and, restoring a channel implies closing a previous channel, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Some Lightning wallets offer backup via email, using Google Drive. In this remote backup system, they send an encrypted version of the channel data whenever it’s updated.
ACINQ’s previous wallet, Eclair, worked this way.
However, the problem with this solution is that it requires an external provider. Phoenix operates differently, using its peers as backups. Since Phoenix only connects with ACINQ’s nodes, controlling backups becomes easier.
But the question remains: will these peers cooperate with me and “return” access to my wallet?
The simple answer is YES, as the Lightning protocol itself has terms that incentivize the other peer to cooperate.
Since Phoenix’s provider, ACINQ, maintains a non-zero reserve in the channels, it always has something to lose. Therefore, to recover your funds in a backup, the wallet only has two options: close and reopen channels, which would generate high costs, or help you recover them easily.
Thus, the second option is more viable.
As a result, Phoenix has implemented a way to recover funds similar to traditional Bitcoin wallets. If something happens to your wallet, such as losing your phone or uninstalling the app, simply download the app again, enter your seed phrase, and you’ll have recovered your funds and previously opened channels.
However, the main challenge in Lightning wallet backups lies in managing open channels with other network participants. So, care must be taken.
Phoenix 2.0
After the initial release of Phoenix in 2019, a new version was developed in 2023, known as the third-generation Lightning wallet.
The latest version retains the strengths of the original while introducing significant improvements.
Dynamic Channels
The main upgrade in Phoenix 2.0 is improved channel management. Previously, users could maintain multiple channels, often leading to frequent new channel openings. This became problematic, as these channels would eventually need to be closed, resulting in high costs.
To address this, Phoenix introduced a technology called splicing, which enables the creation of a single dynamic channel. This simplifies channel management, allowing users to add liquidity as needed without opening new channels.
Previously, opening new channels would surprise users with a 1% fee or a minimum of 3,000 sats. Now, the fee is solely based on the mining cost for the transaction.
When a channel adjustment is necessary, Phoenix can predict if a Lightning payment will incur a channel management fee. Users will be notified in advance.
Check it out:
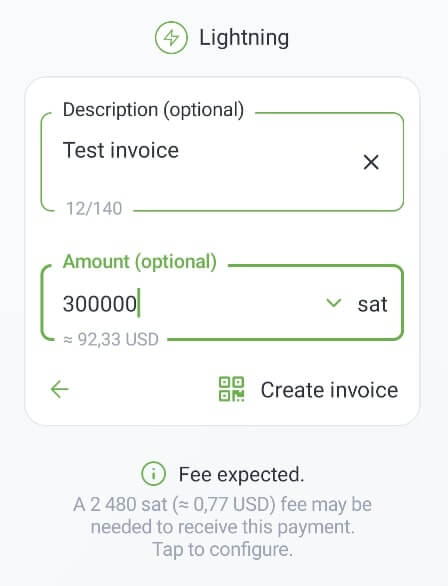
Atomic Swaps
Phoenix has also streamlined the cross-network swap process (e.g., swapping on-chain Bitcoin to Lightning satoshis and vice-versa), known as atomic swaps.
In some services, this process can be complex and rigid for users. Phoenix has automated it and now lets users choose the fee they want to pay.
Ah, and the rates have also changed with this Phoenix update.
Updated fees in Phoenix Wallet
The main change in Phoenix’s latest update is that previously there was a 1% fee on received payments, while now it’s 0.4% on payments made via Lightning.
Below is the complete fee table:
Other Features of Phoenix 2.0
Beyond the updates mentioned, Phoenix also offers unique features not typically found in other Lightning wallets:
- Testnet version (Android only): This version uses test coins that have no real value and are meant for testing purposes only.
- Your wallet is a Lightning node: Phoenix functions as a real and independent Lightning node that runs on your mobile device. You don’t need to run another Lightning node at home or in the cloud.
- It supports the on-chain network: It allows you to send and receive on-chain as a conventional Bitcoin wallet would.
- Liquidity management for channels: You can request an increase in liquidity in your channel and even open additional channels as needed.
How to use the Phoenix Wallet?
Getting started with Phoenix is easy. While it has features for advanced users, it’s designed to be user-friendly for everyone.
Follow these steps to start using the wallet today:
1. Download the Phoenix Wallet
Start by downloading the Phoenix wallet. After a brief introduction, a screen will appear.
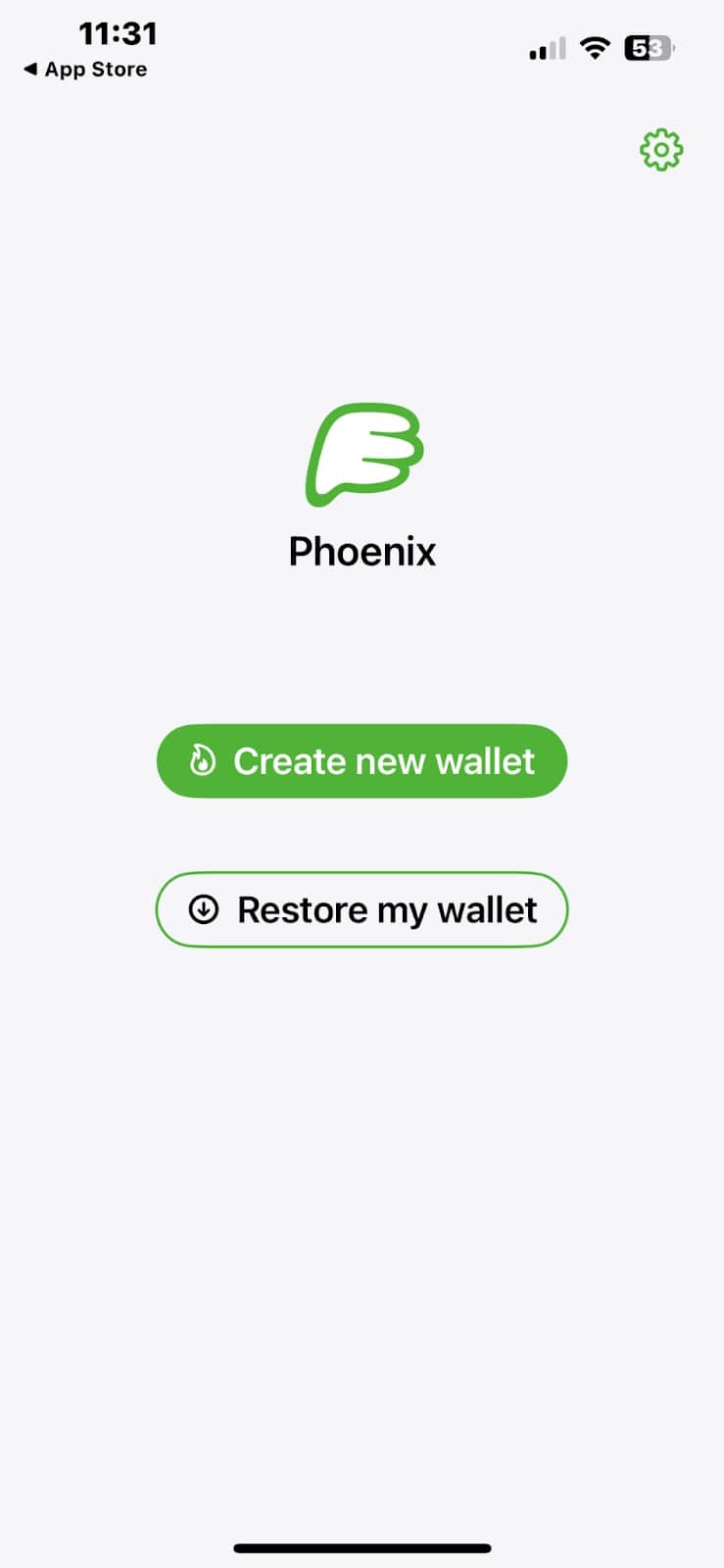
2. Create a new wallet
Select “Create New Wallet”. (Note: For iOS, only English is currently supported.)
3. Access your home screen
Once your wallet is created, you’ll see the home screen.
4. Back up your wallet
Now that your wallet is created, click the gear icon to access settings and go to “recovery phrase” to back up your wallet:
After clicking on Recovery Phrase, the screen below will appear.
To view the seed phrase, click “display seed”, then scroll down and back up your wallet:
5. Send and receive satoshis
To send or receive satoshis, click “Receive” or “Send” on the home screen, and choose the Lightning or on-chain option.
What if my wallet disappears?
A common concern for users of hot wallets (mobile or desktop) is losing access if the wallet disappears or the provider goes out of business.
With governments becoming increasingly regulatory regarding privacy (e.g., the case of Samourai Wallet), many worry about the future of their wallets.
In this regard, if something happens to Phoenix, your funds remain safe, but you won’t be able to move them. The solution is to perform a forced channel closure, which registers your funds on the on-chain network.
To do this, go to your wallet’s settings: Settings > Danger Zone, and click on “Force close channels.”
Phoenix will close the channels unilaterally, and after a wait of about 720 blocks (~5 days), your funds will be transferred back to the on-chain network.
After this, Phoenix recommends you to download the Electrum wallet and recover your funds there (since Phoenix provides your private keys).
Follow these steps:
- Download Electrum.
- Create a new standard wallet.
- Select “I already have a seed.”
- Enter your 12 words, click Options, and check “BIP39 seed.”
- Select “native segwit (p2wpkh).”
- Wait for the funds to appear.
Controversy with the U.S. Exit
In 2024, the founders of Samourai Wallet were detained by the U.S. government, and the wallet’s website was banned. Samourai allowed users to perform coinjoins—a privacy-enhancing technique.
Coinjoin is a coin-mixing tool that lets users create transactions for themselves while mixing the coins in the process, making it more difficult to trace the transactions.
Amid increasing regulatory scrutiny, Phoenix decided to pull its app from U.S. platforms. They advised users to close their channels and withdraw funds by May 3, 2024, when the service was discontinued in the U.S.
This situation highlights the ongoing battle over privacy. Despite this, the wallet continues to operate normally in other countries, like Australia, the UK, and Canada.
Conclusion
Now that you know how to use the Phoenix Wallet and take advantage of its features, you can see how straightforward it is!
As discussed in this article, a wallet can be both simple and powerful, providing tools that support your financial sovereignty.
However, remember that mobile wallets are like pocket wallets you carry around. We don’t recommend storing large amounts in them—after all, you wouldn’t keep all your savings in your everyday wallet, would you?
Also, be mindful of the growing regulatory pressure on wallets and platforms. Choose an option that allows you to recover your funds in case of unexpected events.
I hope this guide has helped you better understand the Phoenix Wallet, and if you found it useful, share it with a friend—it really helps us!
See you next time, and opt out!
Share on your social networks:

Founder of Area Bitcoin, one of the largest Bitcoin education projects in the world, she is a marketer, passionate about technology, and a full-time hands-on professional. She has participated in major Bitcoin conferences such as Adopting Bitcoin, Satsconf, Surfin Bitcoin, and Bitcoin Conference.
Did you like this article? Consider buying us a cup of coffee so that we can keep writing new content! ☕