The process of creating new units of bitcoin is much like searching for gold, hence the concept of bitcoin mining. But unlike gold, mining for bitcoin doesn’t involve digging large holes in the ground or manually searching for precious metal. It’s all done by powerful computers.
How Bitcoin Mining Works
As we mentioned, with gold, miners keep digging until they find the precious metal. On the Bitcoin network, miners try to find the block hash through trial and error until they find the correct combination and close each block of information. These solved calculation blocks are queued in such a way that one block of information is tied to the next block, creating a blockchain.
Once the correct answer is found, the miners present the calculation, the closed block, to the entire network to verify everything is correct. If all checks out, the network moves forward, adding the next block to this chain of information. This entire process is called proof of work, where the entire network follows the calculations of each block and checks that the math is correct and there’s been no cheating. This is how a blockchain reaches consensus on what’s processed on the network.
The miner who first closes the block receives bitcoin as a reward. Today, this reward is 6.25 bitcoins per block, and every four years this reward is cut in half, in an event called halving, reducing the number of bitcoins entering the market.
Bitcoin Miners and Nodes
The logic of the Bitcoin network is like putting together a puzzle. There are 2 types of participants: miners and nodes. Miners are the participants who pick up the puzzle pieces and try to form the game image, and nodes are like that meddling aunt who keeps looking over your shoulder to see if you’ve got the right piece.
When the miner finds the missing piece, everyone can easily see it – just look at the picture and see if the piece was correct or not. It’s a very transparent mechanism, and everyone follows the results in real time.
We use the puzzle analogy because Bitcoin uses game theory. The entire network competes to arrive at the mathematical result first and receive Bitcoin before they run out. Miners are racing against time. This is because there is a limited number of Bitcoins the network can create: 21 million units.
In the 14 years since Bitcoin’s launch, more than 90% of the supply has already been created. The network’s starting point was the most important and profitable time for miners to receive Bitcoin. The start of a blockchain is the most vulnerable period, the network needed to strengthen and decentralize as much as possible. That’s why in the early days of Bitcoin, from 2009 to 2013, anyone with a home computer, a CPU like the one in the picture, could mine and receive many Bitcoins.

It was easy to mine, anyone with a computer could participate in the processing and receive bitcoin as a prize. But once the network matured and more participants entered, the difficulty of these calculations also increased. This is the well-known difficulty adjustment that happens on average every 2 weeks. This means the more participants there are, the more computers compete to solve the blocks.
What is Difficulty Adjustment?
The Bitcoin network adjusts the difficulty of the calculations according to the number of participants. If the network is empty and few people are willing to participate, the algorithm adjusts the calculations to make it easier for people and manage to close the blocks in the predicted time of 10 minutes per block. Therefore, the difficulty adjustment impacts how much computing power (also called hashrate) miners will need to calculate each block. We’ve noticed that this computing power is getting higher and higher:
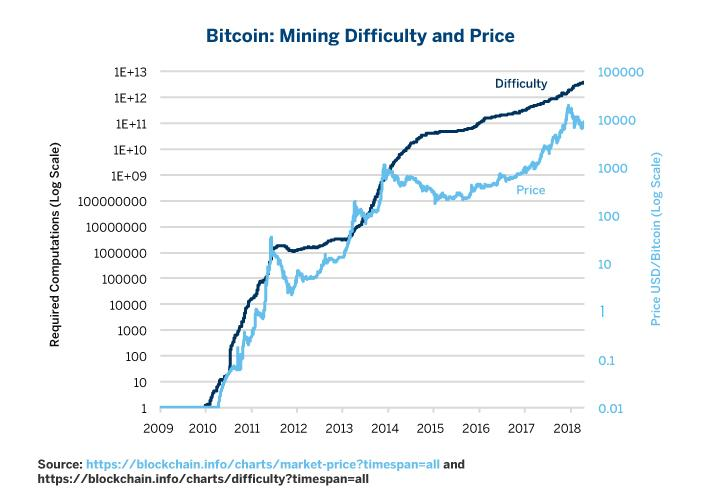
A higher hashrate has some implications: the first is that the network becomes more secure. To attack a network with a high hashrate requires very powerful machines and a lot of energy, which becomes increasingly difficult as the network grows. Over time, computers needed more computing power to perform more complex calculations, which requires more powerful machines and a higher consumption of electrical energy. This is why over time, those who used home computers (CPU) needed to buy dedicated video cards (GPUs, like in the photo below) to mine Bitcoin.

After a while, these GPUs also started not being enough to perform these calculations, as they became increasingly difficult. Thus, an entire mining industry was created around Bitcoin, and specific machines were developed for this purpose: ASICs.

An ASIC is the dream of many Bitcoiners and it takes several of these machines to have strong enough computing power to compete with the rest of the network and secure Bitcoin. These machines are usually housed in gigantic warehouses with thousands side by side, working day and night mining.
Is it possible to mine from home?
Bitcoin mining today is a major industry because mining requires a heavy investment in infrastructure. You need specific machines (ASICs), as well as a cooled environment to prevent overheating, maintenance, and management of electricity costs.
In many countries, it’s hard to find Bitcoin miners because of the high cost of electricity. Miners usually set up their base in countries with abundant and cheap electricity, like Paraguay, or in cold places where you don’t need coolers to cool down the machines, which would already be a cost less, like Iceland. There are also regions that encourage mining, such as Texas (USA).
However, if you have the money to cover this high fiat cost and the patience to hold and wait for Bitcoin to appreciate over the next decades, this DCA without KYC might be worthwhile. You need to do the math, put it down on paper and see if it makes sense for you.
Can miners steal Bitcoin for themselves?
That would be the biggest self-sabotage for miners and, again, game theory appears to bring logic to the situation.
The Bitcoin network was created so that all participants cooperate with each other and are rewarded for protecting and running the network. Therefore, any contrary action either has no effect or ends up not being worthwhile for the malcontent.
Miners are dependent on the Bitcoin network. Therefore, they are the last ones interested in changing how it operates, as it would impact their rewards.
Indeed, if a miner starts behaving erratically, other miners will start invalidating the data processed by the unstable one.
Most miners are interested in protecting the network because if the network starts to malfunction, Bitcoin itself will lose its value and the miners’ work ends. The Bitcoin network uses game theory to run and to encourage miners to be guardians of the network and always protect their livelihood. In addition, any suspicious movement is immediately detected by the nodes and communicated to the network. Just like putting a piece from another game into the puzzle, that meddling aunt who just watches and checks will alert everyone that you’re cheating.
These nodes are run by people around the world, and you can even run one from your home computer. You don’t receive Bitcoin as a reward for running a node as miners do, but you have the power to monitor the network, to be the whistle-blower if someone decides to cheat in the game. These nodes ensure decentralization and help protect the Bitcoin network.
Mining Market Evolved
Unless you want to invest in a mega mining farm in another country and focus on that, mining Bitcoin with few resources and without understanding these technical details is not worth it.
Don’t be deceived, this market has already evolved quite a lot and is no longer just a nerd thing where you just plug in your computer and make a fortune. It’s a market that is increasingly advanced and professional. Mining has become a mega business and there are even Bitcoin mining company shares on NASDAQ.
From our perspective, if your focus is to benefit from Bitcoin’s exponential rises, the answer is simple: learn how to invest in Bitcoin and save it safely in the long run so that you can enjoy the Bitcoin standard in the future.
Share on your social networks:
Area Bitcoin is an educational Bitcoin school that aims to accelerate the financial and intellectual sovereignty of all individuals.
Did you like this article? Consider buying us a cup of coffee so that we can keep writing new content! ☕







